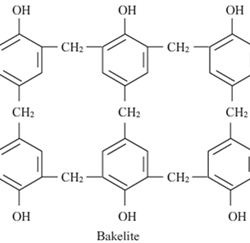
Types of Polymerization Reactions
1. Addition polymerization (or) chain growth polymerization: ⇒ The molecules of the same monomer or different monomers add together on a large scale to form a polymer. ⇒ The monomers used are unsaturated compounds. Eg: Alkenes, alkadienes and their derivatives. ⇒ Can take place through the formation of either free radicals or ionic species. Free Read more about Types of Polymerization Reactions[…]