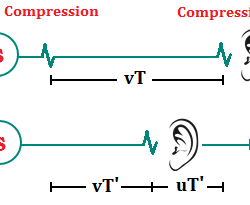
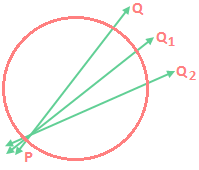
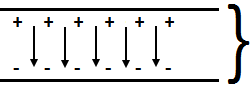
Temperature dependence of the rate of a reaction
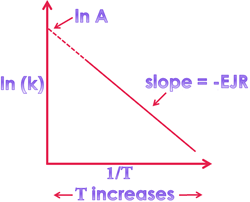
1. Effect of temperature on reaction rate: ⇒ As the temperature increases, the average energy of the reaction increases, hence rate of reaction increases. ⇒ As a common rule, for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate of reaction will increase by 2 (or) 3 times of initial value. ⇒ According to Arrhenius concept: η Read more about Temperature dependence of the rate of a reaction[…]