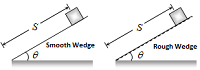
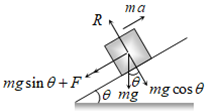
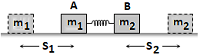
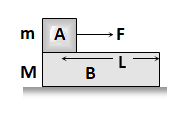
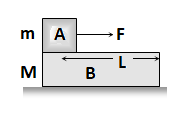
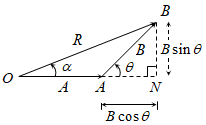
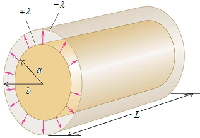
Thermal Capacity
Thermal Capacity Thermal Capacity of a substance is defined as the amount of heat required to change its temperature through one degree. If Q is the amount of required to change the temperature of a body of mass m through, then Q = msΔθ If temperature difference = 1, then Q = ms The value Read more about Thermal Capacity[…]