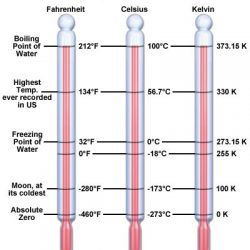
Combination or Propagation of Errors
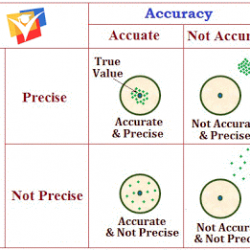
Generally, the result of an experiment is obtained by doing mathematical operations on several measurements. Obviously, the final error depends not only upon the errors in individual measurements but also on the nature of mathematical operations. Following are the rules for combination of errors. (a) Errors in a Sum or Difference: Let there be two Read more about Combination or Propagation of Errors[…]