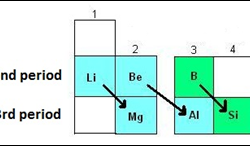
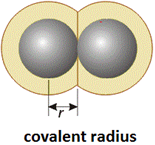
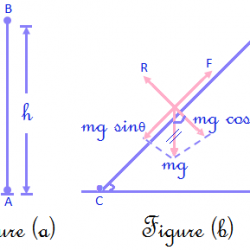
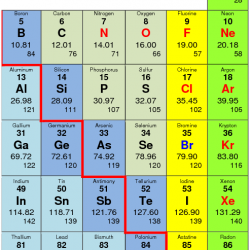
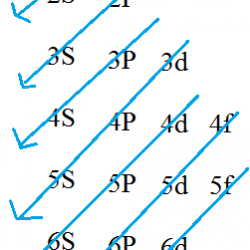
Trends in Chemical Properties of Periodic Elements
Ionisation Energy: It is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the outermost orbit of an isolated gaseous atom. (If given in terms of the amount of work done in removing an electron, the property is called ionization potential.) Units: kJ / mol (for ionization potential, units: eV/atom.) This is denoted by word I. Read more about Trends in Chemical Properties of Periodic Elements[…]