Fundamental Concepts of Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms II
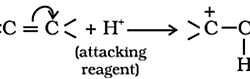
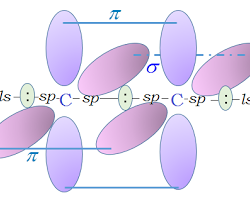
Inductive Effect: The polarization of σ bond due to electron withdrawing or electron donating effect of adjacent groups or atoms is called inductive effect. Salient features of inductive effect: It arises due to electronegativity difference between two atoms forming a sigma bond. It is transmitted through the sigma bonds. The magnitude of inductive effect decreases while moving Read more about Fundamental Concepts of Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms II[…]