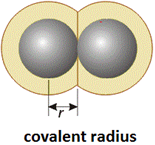
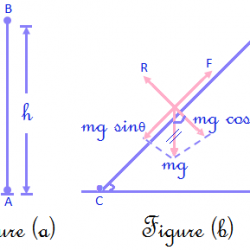
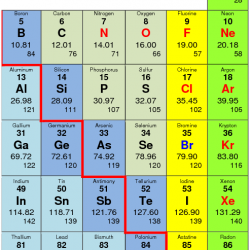
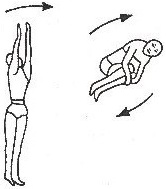
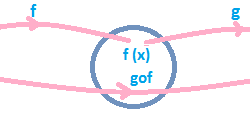
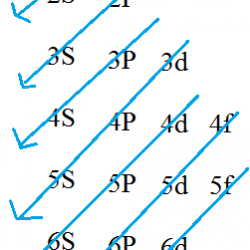
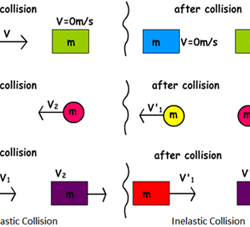
Intervals
Closed Interval: Let a and b be two given real numbers such that a < b. Then the set of all real numbers x such that a ≤ x ≤ b is called a closed interval and is denoted by [a, b] i.e., [a, b] = {x ϵ R| a ≤ x ≤ b} Open Read more about Intervals[…]