Principles of Calorimetry
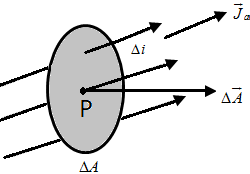
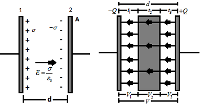
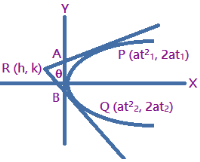
Principles of Calorimetry Calorimetry is a scientific experimental measurement of the change of heat of a substance. A calorimeter is usually the container in which the heat change experiment is conducted. Calorimetry means “measuring heat”. When two bodies (one being solid and other being liquid or both being liquid) at different temperatures are mixed, heat Read more about Principles of Calorimetry[…]