Vector – Equation of a Plane
Equation of the Plane that Passes through Point A with Position Vector \(\vec{a}\) and is Parallel to given Vector \(\vec{b}\) and \(\vec{c}\):
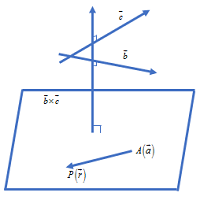
Vector form: Let \(\vec{r}\) be the position vector of any Point P in the plane.
Then \(\overrightarrow{AP}=\overrightarrow{OP}-\overrightarrow{OA}=\vec{r}-\vec{a}\),
Since vectors \(\vec{r}-\vec{a}\), \(\vec{b}\) and \(\vec{c}\) are coplanar,
we have \(\left( \vec{r}-\vec{a} \right).\left( \vec{b}\times \vec{a} \right)=0\),
\(\vec{r}.\left( \vec{b}\times \vec{a} \right)-\vec{a}.\left( \vec{b}\times \vec{a} \right)=0\),
\(\vec{r}.\left( \vec{b}\times \vec{a} \right)=\vec{a}.\left( \vec{b}\times \vec{a} \right)\),
\(\left[ \overrightarrow{r}\,\,\overrightarrow{b}\,\,\overrightarrow{c} \right]=\left[ \overrightarrow{a}\,\,\overrightarrow{b}\,\,\overrightarrow{c} \right]\),
Which is the required equation of the plane.
Cartesian Form: From \(\left( \vec{r}-\vec{a} \right).\left( \vec{b}\times \vec{a} \right)=0\),
We have \(\left[ r-\overrightarrow{a}\,\,\overrightarrow{b}\,\,\overrightarrow{c} \right]\),
\(\left[ \begin{matrix}
x-{{x}_{1}} & y-{{y}_{1}} & z-{{z}_{1}} \\ {{x}{2}} & {{y}{2}} & {{z}{2}} \\ {{x}{3}} & {{y}{3}} & {{z}_{3}} \\\end{matrix} \right]=0\),
Which is the required equation of the plane
Where \(\vec{b}={{x}_{2}}\hat{i}+{{y}_{2}}\hat{j}+{{z}_{2}}\hat{k}\) and \(\vec{c}={{x}_{3}}\hat{i}+{{y}_{3}}\hat{j}+{{z}_{3}}\hat{k}\).
