Young’s Double Slit Experiment
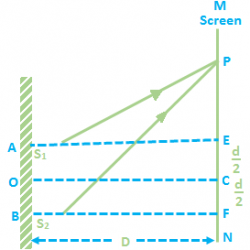
Young’s double slit Experiment Young’s interference experiment, also called Young’s double-slit interferometer, was the original version of the modern double-slit experiment, performed at the beginning of the nineteenth century by Thomas Young. This experiment played a major role in the general acceptance of the wave theory of light. Young’s double slit experiment uses two coherent sources of light placed at a small distance Read more about Young’s Double Slit Experiment[…]