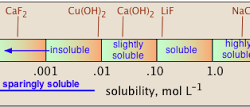
Solubility Equilibria of Sparingly Soluble Salts
The solubility depends on a number of factors important amongst which are the lattice enthalpy of the salt and the solvation enthalpy of the ions in a solution. For a salt to dissolve in a solvent the strong forces of attraction between its ions (lattice enthalpy) must be overcome by the ion-solvent interactions. The solvation Read more about Solubility Equilibria of Sparingly Soluble Salts[…]