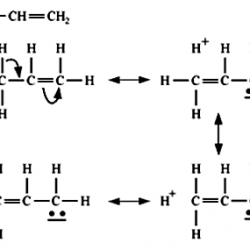
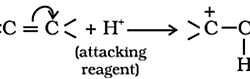
Methods of Preparation of Acetylene
Preparation methods 1. From calcium carbide: Ethyne is prepared by calcium carbide with water. CaC₂ + 2H₂O → Ca (OH)₂ + C₂H₂ 2. From vicinal dihalides: Vicinal dihalides on treatment with alcoholic potassium hydroxide undergo, dehydrohalogenation one molecule of hydrogen is eliminated to form alkenyl halide which on treatment with sodalime gives alkyne. Some Other General Methods Read more about Methods of Preparation of Acetylene[…]