Ohm’s law
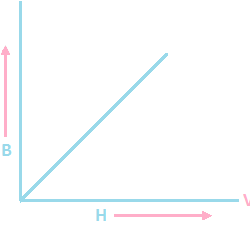
General form of Ohm’s law: At a constant temperature potential difference across a conductor is directly proportional to the current passing through it V α I V = RI Ohm’s law is material dependent because it is defining resistance of the material. Those which obeys ohm’s law and are known as ohmic or linear conductor, Read more about Ohm’s law[…]