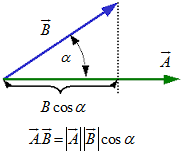
Collisions
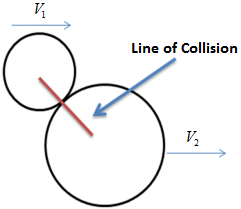
Collisions Collision is an event that demands involvement and interaction of at least two objects. In course of occurrence of such event interaction amongst object occur and each object experiences impulsive forces – a force which occur for a very small duration, from other. This impulsive force is responsible for change in momentum of the object Read more about Collisions[…]