Speed of Wave Motion
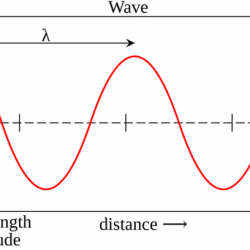
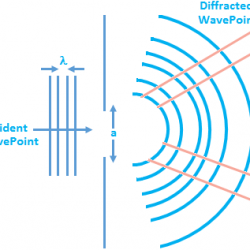
Speed of Wave Motion A wave is a disturbance that moves along a medium from one end to the other. If one watches an ocean wave moving along the medium (the ocean water), one can observe that the crest of the wave is moving from one location to another over a given interval of time. The crest Read more about Speed of Wave Motion[…]