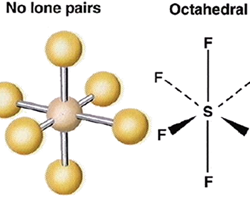
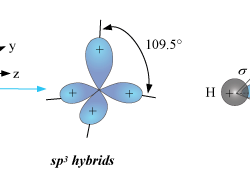
Intermolecular forces
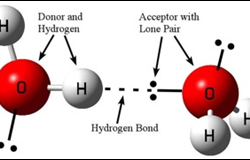
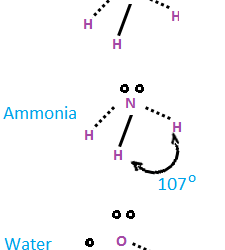
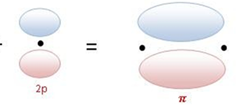
Forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting atoms/molecules other than electrostatic or covalent bonds are called inter molecular forces. Attractive inter molecular forces: Known as van der Waal’s forces Types: 1. Dispersion forces/ London forces: Force of attraction between temporary dipoles. Always attractive. Significant only at short distances between interacting particles Magnitude depends on polarizability Read more about Intermolecular forces[…]