Fundamental Rules for Differentiation
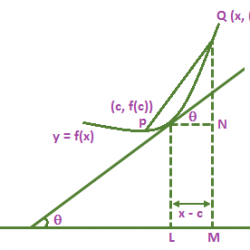
Fundamental Rules for Differentiation Rule (I): Differentiation of a constant function is zero i.e., . Rule (II): Let f(x) be a differentiable function and let c be a constant. Then c.f(x) is also differentiable such that . This is the derivative of a constant times a function is the constant times the derivative of the Read more about Fundamental Rules for Differentiation[…]