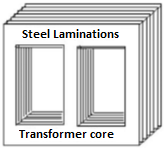
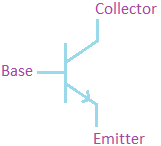
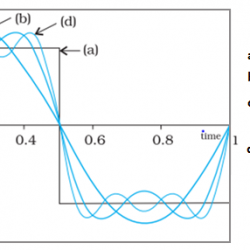
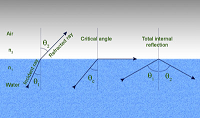
Coulomb’s Law
Coulomb’s Law The study of electrostatics begins with the Coulomb’s law. It is an experimental law published in 1785 by French physicist Charles Augustin de Coulomb. This law is very important for the development of theory of electromagnetism. Charles Coulomb observed that when two electric charges are placed close to each other, they experience a force. He Read more about Coulomb’s Law[…]