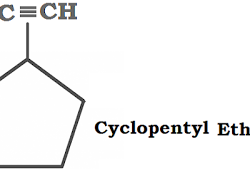
Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells
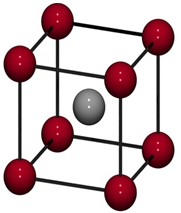
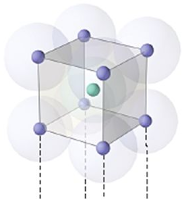
Crystal lattice is the depiction of three dimensional arrangements of constituent particles (atoms, molecules, ions) of crystalline solids as points. Characteristics of crystal lattice: Each constituent particle is represented by one point in a crystal lattice. These points are known as lattice point or lattice site. Lattice points in a crystal lattice are joined together Read more about Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells[…]