Slope (Gradient) of a Line
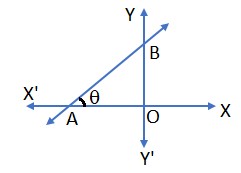
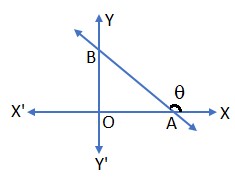
Slope of a Line: A line in a coordinate plane form two angles with the x – axis which are supplementary. The angle (say) θ made by the line with the positive direction of the x – axis and measured anticlockwise is called the inclination of the line. The trigonometric tangent of this angle is called the slope (or) gradient of the line.
Note:
- The slope of a line generally denoted by m. thus, m = tanθ
- Since a line parallel to the x -axis makes an angle of 0° with the x – axis, its slope is tan0° = 0
- A lie parallel to the y – axis i.e., perpendicular to the x – axis makes an angle of 90°with the x – axis.
So, its slope is tanπ/2 = ∞
- The slope of a line equally inclined with the axis is 1 or -1, as it makes an angle of either 45° or 135° with the x – axis.
