A locus is a set of points which satisfy certain geometric conditions. Many geometric shapes are most naturally and easily described as locus. For example, a circle is the set of points in a plane which are a fixed distance from a given point the center of the circle.
Example: A locus
The following diagrams give the locus of a point that satisfy some conditions.
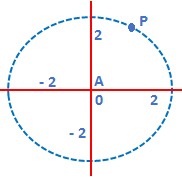
Locus of points equidistant from a point A will form a circle with center A. |
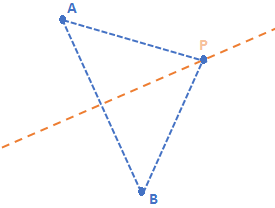
Locus of points that are equidistant from two lines will be bisect the angle formed by the two lines. |
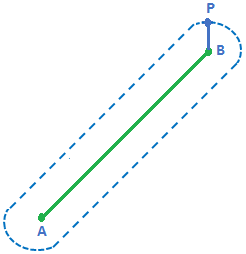
Locus of points equidistant from a line segment. |
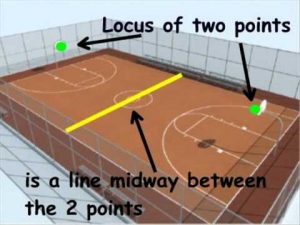
Locus of points equidistant from two points A and B forms a perpendicular bisector of the line AB. |
A step-by-step procedure for finding plane locus:
Step 1: If possible, choose a coordinate system that will make computations and equations as simple as possible.
Step 2: Write the given conditions in mathematical form involving the coordinates.
Step 3: Simplify the resulting equation.
Step 4: Identify the shape cut out by the equation.
1. Find the point on the x-axis, which is equidistant from (7, 6) and (-3, 4).
Sol: Let A (7, 6), B (-3, 4)
Let P(x, 0) be the point on x-axis which is equidistant from A and B.
Then PA = PB ⇒ PA² = PB²
⇒ (x – 7)² + (0 – 6)² = (x + 3)² + (0 – 4)²
⇒ x² – 14x + 49 + 36 = x² + 6x + 9 + 16
⇒ -14x + 85 = 6x + 25 ⇒ 20x = 60
⇒ x = 3
The required point is P (3, 0).
