Preparation:
- 4BH3 + 3LiALH4 → 2B2H6 + 3LiF + 3AlF3
- 2NaBH4 +I2 → B2H6 + 2NaI + H2
- 2BF3 + 6NaH → B2H6 + 6NaF
Structure:
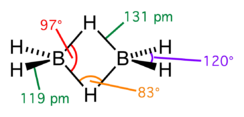
- Diborane contains four terminal and two bridging hydrogen atoms
- The terminal H atoms and B atoms lie in one plane. The bridging H atoms lie above and below the plane
Properties:
- Colourless highly toxic gas
- B.P : 180 K
- Catches fire instantly in air
- Burns in oxygen releasing energy.
B₂H₆ + 3 O₂ → B₂O₃ + 3 H₂O; ΔcHΘ = -1976 kJ/ mol - Hydrolyze in water to give boric acid
B₂H₆ + 6H₂O → 2B(OH)₃ + 6 H₂ - Borane adducts:
B₂H₆ + 2NMe₃ → 2BH₃.NMe₃
B₂H₆ + 2CO → 2BH₃.CO - On reaction with ammonia and subsequent heating, gives borazine also known as inorganic benzene.
3B₂H₆ + 6NH₃ → 3[BH₂(NH₃)₂]+[BH₄]– → 2B₃N₃H₆ + 12H₂
Borazine