Capacitor
The capacitor is a component which has the capacity to store energy in the form of an electrical charge producing a potential difference across its plates, much like a small rechargeable battery. There are many different kinds of capacitors available from very small capacitor beads used in resonance circuits to large power factor correction capacitors, but they all do the same thing, they store charge.
What is a Capacitor?
A Capacitor is an electronic device or component like resistor used in various electronic and electrical circuits and devices. The property of a capacitor to store electrical energy in the form of static electricity makes it useful for various purpose in electronics and electrical engineering. The capacitor is also known as Condenser. A capacitor has two parallel metal plates which are not connected to each other. The two plates in the capacitor are separated by insulating medium, this medium is commonly known as Dielectric.
There are different types and different shapes of capacitors available, from very small capacitors which are used in resonance circuits to large capacitors for stabilising HVDC lines. But all capacitors are doing the same work that is storing the electrical charge.
The shape of a capacitor is rectangular, square, circular, cylindrical or spherical shape. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. As the different types of capacitors are available different symbols were available to represent them. Those are
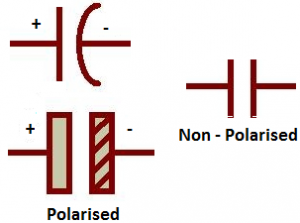
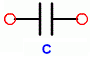
In an electrical circuit diagram, a capacitor is usually denoted by letter “C” by two parallel lines similar to a parallel plate capacitor.
Applications of Capacitor: A capacitor is used for various purpose in electrical circuits and devices. The applications for which the capacitors are mostly used includes Energy storage, Power Conditioning or Factor Correction, Signal coupling, Decoupling, Oscillators, Audio signals and noise filter, motor starter and tuners.
