Ever wondered how it would be to learn few important reactions in a very less time?? Here you go guys about cannizaro reaction, its types and mechanism.
1. Intramolecular cannizaro reaction: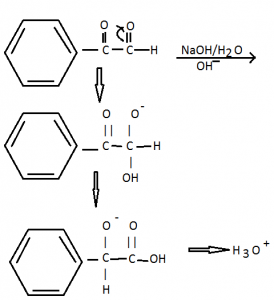 This is an example of intermolecular reaction.
This is an example of intermolecular reaction.
This reaction is redox and disproportion reaction.
2. Intermolecular condensation:
\(H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,+Ph-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-H\xrightarrow{NaOH/{{H}_{2}}O}H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-H+\overset{+}{\mathop{NaOH}}\,\).
\(H-\underset{OH}{\overset{{{O}^{-}}}{\mathop{\underset{|}{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}}\,}}}\,-H\xrightarrow{NaOH}H-\underset{{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}}{\overset{{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}}{\mathop{\underset{|}{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}}\,}}}\,-H\).
\(H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-{{O}^{-}}N{{a}^{+}}\) and \(Ph-C{{H}_{2}}^{-}{{O}^{-}}Na+\,{{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}\to H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-OH+Ph-C{{H}_{2}}-OH\).
i) NaOH will attack on carbon of formaldehyde because, carbon of formic acid is more acidic
ii) Due to +R effect ofph- group the acidity of carbon in pheryl aldehyde decreases
Trick:
⇒ In cannizzarro reaction, one compound gets oxidizes & the other gets reduced.
⇒ Generally the compound with more acidic carbon gets oxidized & the one with less acidic gets reduced.
\(H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,+Ph-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,\).
⇒ In a mixture of formaldehyde & phenyl aldehyde, when formaldehyde reacts with phenyl aldehyde reacts with phenyl aldehyde then it is called cross cannizzaro reaction. When
\(H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,H\,or\,Ph-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,H\).
⇒ Reacts with themselves then it is known as ‘self-cannizzarro reaction’.
Self-cannizzarro reaction:
\(H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-H+H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,\xrightarrow{NaOH/{{H}_{2}}O}H-\underset{OH}{\mathop{\underset{|}{\mathop{\overset{{{O}^{-}}}{\mathop{\overset{|}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,}}\,}}\,-H+H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-H\xrightarrow{NaOH/{{H}_{2}}{{O}^{+}}}H-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-OH+C{{H}_{3}}OH\).
\(Ph-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,+Ph-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{CH}}\,}}\,\xrightarrow{NaOH/{{H}_{2}}O}Ph-\overset{O}{\mathop{\overset{||}{\mathop{C}}\,}}\,-OH\).
(One part will get oxidized and other gets reduced)
So 4 possible products by self & cross cannizzaro reaction
Self cannizzaro & intramolecular are both redox & disproportionation whereas cross Cannizzaro is an only redox reaction
Trick:
1) In condensation reactions a new carbon-carbon bond formation takes place while in case of cannizzaro reaction oxidation- reduction takes place
2) Cannizzaro reaction ⇒ possible only for Benzaldehydes & formaldehyde (those aldehydes which do not have alpha-hydrogen)
3) Aldol condensation ⇒ possible only for aldehydes having at least on alpha- hydrogen
4) Cross aldol condensation ⇒ possible for 2 different aldehydes having at least one alpha-hydrogen
[Note: exception is Benzaldehyde & other aldehyde having at least one alpha-hydrogen].
