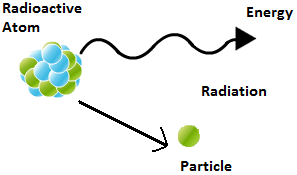
Radioactivity
An atom is made up of three fundamental subatomic particles protons, neutrons and electrons. Out of these three particles, protons and neutrons located at the centre of the atom as a hard and dense part known as nucleus. The rest of the part of atom contains negatively charged particles called as electron which balance out the charge of the protons and make the atom electrically neutral.
The total mass of an atom accumulate at the centre of atom in the form of nucleus as the mass of electrons is negligible. Hence, the sum of the total number of protons and neutrons is called as mass number.
There must be some nuclear force which maintains the existence of nucleus, because there is a repulsion force between positively charged protons which are collected in a small region of nucleus. If the number of proton is less in an atom, other forces can hold the protons together and atom becomes stables. But as the ratio of protons to neutrons is increases, protons cannot be held firmly together and hence form an unstable nucleus.
What is Radioactivity?
Atoms become unstable due to large neutron to proton ratio. Such unstable nucleus emitted some radiations and convert in to some other stable nucleus and known as radioactive elements. These radiation are termed as radioactive rays. Generally these radiations consist some particles like alpha and beta particle in some time charge less gamma rays emitted.
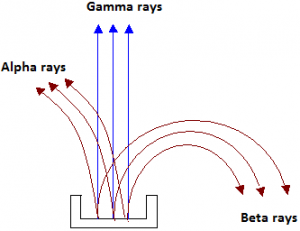
- For convenience, Rutherford called the three types of radiation alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) rays. The alpha-rays were deflected in a direction opposite to that of beta-rays.
- This showed that the αα-rays carried a positive charge, β-rays carried a negative charge and those which passed un-deviated were neutral or uncharged were γ-rays.
- Similarly, if the radiations given out by a radioactive substance are subjected to an electric field perpendicular to their path, they separate into three constituents.
- Those which turn towards the negative plate are the positively charged alpha particles.
- Those, which turn towards the positive plate, are the negatively charged beta particles.
- Those, which pass un-deviated, are the uncharged gamma radiations.
- Further investigation has shown that an alpha ray is a stream of helium nuclei, a beta ray is a stream of electrons and a gamma ray is an electromagnetic radiation whose frequency is higher than that of X-rays.
Radioactivity Definition: The property of emission of radioactive rays from radioactive elements is termed as radioactivity.
Generally, elements with atomic number more than 82 show radioactivity and disintegrated to small nuclei with the emission of alpha, beta, proton, neutron particles or gamma rays. This nuclei with decomposed is called as parent nuclei and the product nuclei is termed as daughter nuclei. The atomic number and mass depends upon the type of radioactive rays emitted during nuclear reaction. The decay of radioactive parent nuclei to stable nuclei is known as radioactive decay or nuclear decay.
The type of decay depends on the type of radioactive particles emitted in decay. For example,
- Alpha decay
- Beta decay
- Gamma decay
Who discovered Radioactivity?
On 22 December, 1895; Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered Roentgen rays, later termed as X-rays. In 1896, A French physicist, Henri Becquerel who was aware about the discovery of X-rays, found that a photographic plate wrapped in a thick black paper which had been placed by chance in the same drawer which contained uranium salts, had become affected or fogged.
He concludes that uranium slats emitted some radiation like X-rays which can causes ionization in air. He called these rays as radioactive rays and this property as radioactivity.
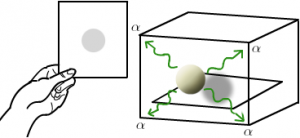
The husband and wife team of Pierre and Marie Curie were aware about the Henri Becquerel experiment and study with their own uranium-containing ores. They proposed the term “radioactivity” which was the spontaneous emissions of radiation from certain elements. These elements called as radioactive elements. They studied some radioactive components like uranium and discovered two new radioactive elements which they named polonium and radium. The next important step on the road of discovery of radioactivity was taken by Ernest Rutherford in 1904. He established the concept that the rays emitted by the radioactive substance are of three types designated as alpha, beta and gamma rays. He purposed the concept of nucleus in an atom by using Gold foil experiment and interpreted that an atom was made up of mostly empty space with a small dense portion at centre which deflected the positively charged alpha particles.
